5. Cryptography
Keywords
- Encryption - Encoding data so that only sender or receiver can read the data or anyone with key.
- Hash - Ensure integrity of data
- Authentication is any process by which a system verifies the identity of a user who wishes to access it.
- Non-repudiation is a way to guarantee that the sender of a message cannot later deny having sent the message and that the recipient cannot deny having received the message.
- Palintext - An unencrypted message (clear text)
- Ciphertext - An encrypted message
- Cipher - The algorithm use to encrypt/decrypt
- Cryptanalysis - Art of cracking encryption
Cryptography
Crypto = hidden secret
graphy = To write
A technique of encrypting (converting) clear text data into a scrambled code. This ensure CIA traids and non-repudation.
The encrypted data is called Ciphertext.

Types
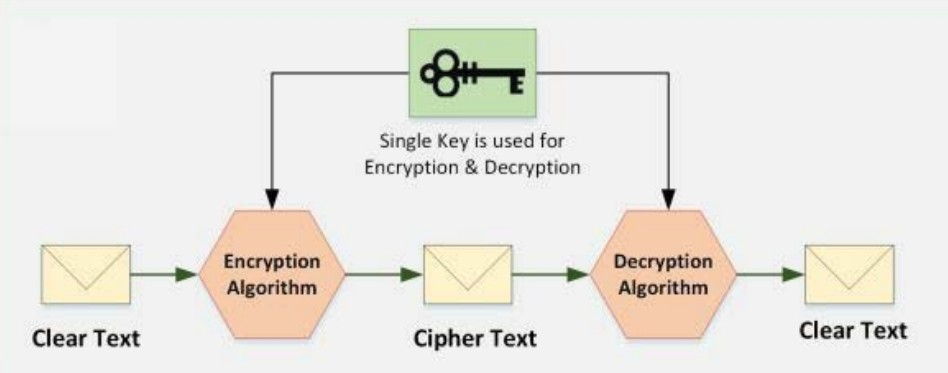
- Symmetric Cryptography
It is based on a shared secret (key) that is used for both encryption as well as decryption. Both parties share the same key. Ex: DES,3DES,AES
- Keys
Just like a lock has a key, every encrypted data has a key which decrypts it.
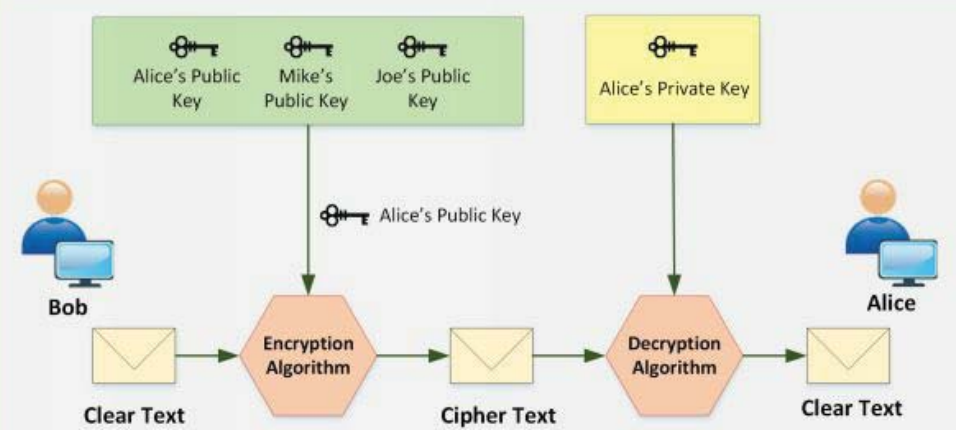
- Asymmetric / Public key Cryptography
In it 2 keys are used.
Public key - known to everyone
Private key - kept as secret - known to owner only
Only Private key can decrypt something encrypted with public key and vice versa.
Ex: RSA,DSA,Diffie-Hellman Algorithm
Digital Certificates
They verify that a particular public key belongs to a certain entity (ownership of the key).
The public key is present inside the digital certificate.
PKI (Public Key Infastructure)
It is a system for the creation, storage, and distribution of digital certificates.
A CA (Certificate or Certification Authority) issues digital certificates.
Root Certificate
It provides the public key and other details of CA (Certificate Authority).
PKI Components:
- A Certificate Authority (CA), which acts as “the root of trust”. The CA issues digital certificates representing the ownership of a public key.
- A Registration Authority (RA) or subordinate CA - validates the registration of a digital certificate with a public key. Every time when a request for verification of any digital certificate is made, it goes to RA.
- A central directory - i.e., a secure location in which keys are stored and indexed;
- A certificate management system managing things like the access to stored certificates or the delivery of the certificates to be issued;
- A certificate policy stating the PKI's requirements concerning its procedures. Its purpose is to allow outsiders to analyze the PKI's trustworthiness.